The world is watching in shock as a nuclear drama unfolds in northeastern Japan. In only a few days, most of us have somehow come to accept that there are degrees of a nuclear meltdown and that explosions at a nuclear power plant may not always point to a cataclysmic outcome. A week ago, those beliefs would have been unthinkable. Then, nuclear power was a binary condition: it was either safe, clean and efficient, or it was Chernobyl, with no in between.
Even in the safest of times, generating power through nuclear energy presents major challenges. One of the key challenges is handling the inevitable nuclear waste, primarily spent nuclear fuel. After conducting extensive studies in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the U.S. Government thought it had found an answer. In 1983, the U.S. Government contracted with operators of nuclear power plants to begin picking up nuclear waste starting in 1998 and storing it in a central facility.
The U.S. Government had then agreed to become the primary shipping and storage mechanism for the nuclear power industry. The plan was to store nuclear waste at the now defunct Yucca Mountain storage facility located about 100 miles from Las Vegas. Ultimately, fears of geologic instability at the site combined with election-year politics doomed the project. So, instead of one underground facility located on the site where 904 atomic bomb tests have already been conducted, America is left with more than 100 storage sites around the country where nuclear waste is stored in pools or barrels.
When the U.S. Government breached their agreement to pick up the nuclear waste, operators of nuclear power plants sued. In this line of cases, the question is not whether a breach has occurred, but rather how much it will cost the facility to store the waste if that is even possible. Animators at Law has been involved in quite a number of these spent fuel cases typically heard in the U.S. Court of Federal Claims. Below are some litigation graphics from these cases.
The animation below shows the removal of a reactor pressure vessel. When a plant must be closed due to age or due to an inability to store more waste, the reactor pressure vessel may be removed. The boiling water reactors at Japan's Fukushima nuclear power plant use a similar reactor pressure vessel. Originally created in PowerPoint using dozens of technical illustrations played in succession, this litigation animation shows two methods of removing the reactor pressure vessel that contains the plant's nuclear core.
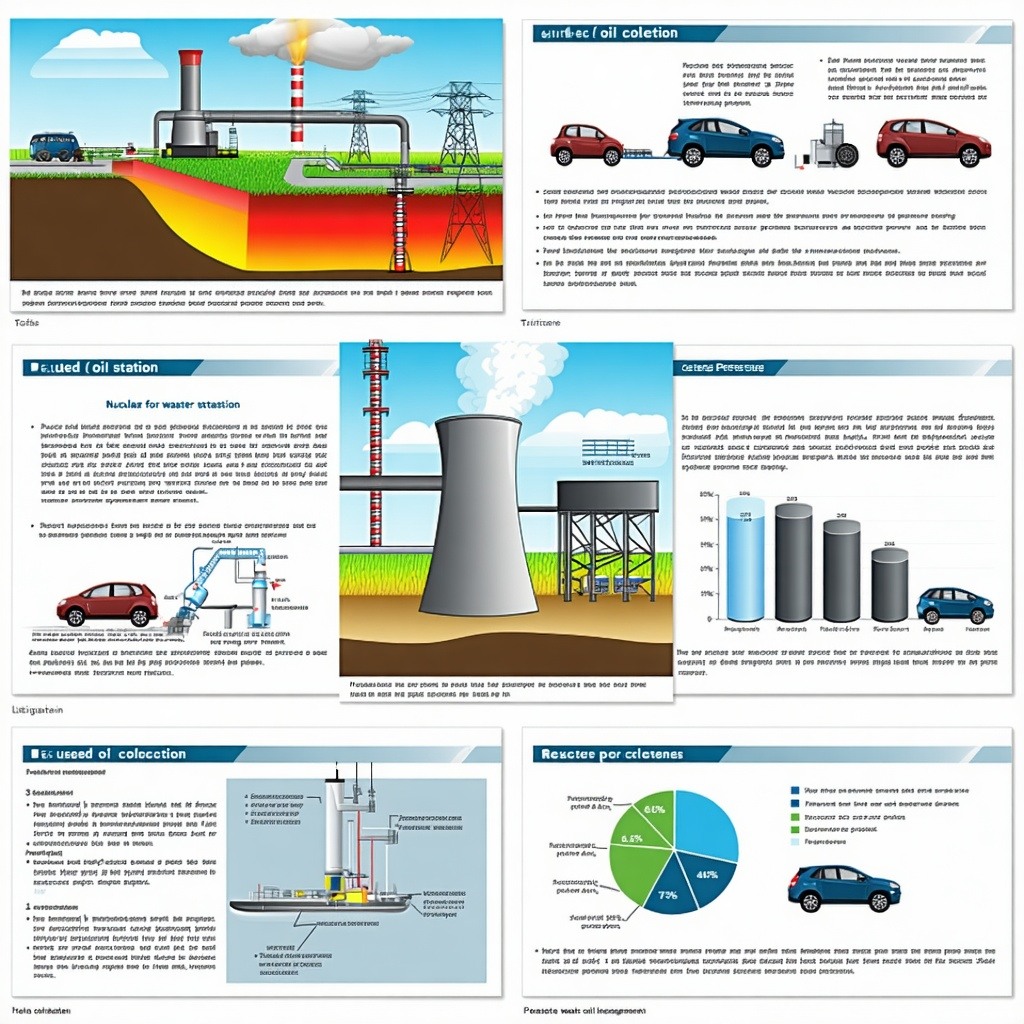
The trial exhibits below are shown as a screen capture of some PowerPoint litigation graphics. These trial exhibits analogize the problem an automobile service station would have if its used oil collection stopped to the spent nuclear fuel storage problem faced by nuclear power plant operators. Further, it helps make the case that costs do not stop with storage (as the U.S. Government contends) but also include indirect and overhead costs related to storage (e.g. security, accounting and management).
Animators at Law has helped its clients recover hundreds of millions of dollars in spent nuclear fuel litigation cases, and effective litigation graphics have been key to this success.
For more on how nuclear power works: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_Power
To learn more about the crisis in Japan or to make a donation: http://www.google.com/crisisresponse/japanquake2011.html




Leave a Comment